Although the sector as a whole has traditionally been comparatively wary of the ever-increasing pace of technology, legal services are increasingly data driven, with an abundance of AI-related discussion emerging within legal technology circles. The core Document Management Systems (DMS) and Practice Management Systems (PMS) remain the centre of focus for how and where to deploy a variety of rapidly maturing SaaS platforms, or dedicated, highly customised suites.
The UK government has proposed extending its ban on ransomware payments to cover the entire public sector in an attempt to deter cybercriminal attacks and protect taxpayers.
Stoli Group USA, the US subsidiary of vodka maker Stoli, has filed for bankruptcy – and a ransomware attack is at least partly to blame.
The American branch of Stoli, which imports and distributes Stoli brands in the United States, as well as the Kentucky Owl bourbon brand it purchased in 2017, was hit by a ransomware attack in August 2024.
Although the rise in money criminals have generated through ransomware has risen by what may appear to be a small percentage amount (approximately 2% from US $449.1 million to US $459.8 million), this is in spite of disruption caused to ransomware-as-a-service operations such as LockBit and ALPHV/BlackCat by law enforcement agencies.
The figures for the first half of 2024 include the US $75 million reportedly paid to the Dark Angels ransomware gang by an undisclosed Fortune 50 company, in what was believed to be the largest ever single ransom payment made since records began.
The ballooning size of maximum ransom payments represents a 96% year-on-year growth from 2023, and a 335% increase from the maximum payment made in 2022.
Chainalysis's research reveals that the median ransom payment made in response to the most severe ransomware has rocketed from just under US $200,000 in early 2023 to US $1.5 million by mid-June 2024.
The researchers believe that this 7.9x increase in the typical size of ransom payment (a nearly 1200x rise since the start of 2021) suggests that larger businesses and critical infrastructure providers considered more likely to agree to make higher payments due to their greater access to funds and the more significant impact of downtime.
Against this backdrop, the study claims that ransomware victims are giving in to extortion demands less often. As it explains:
Posts to ransomware leak sites as a measure of ransomware incidents have increased YoY by 10%, something we would expect to see if more victims were being compromised. However, total ransomware payment events as measured on-chain have declined YoY by 27.29%. Reading these two trends in tandem suggests that while attacks might be up so far this year, payment rates are down YoY. This is a positive sign for the ecosystem signalling that perhaps victims are better prepared, negating the need to pay.
In short, ensuring that your organisation had prepared to respond to a ransomware attack is essential.
Many organisations underestimate the importance of having a robust incident response plan. But knowing how to respond, especially in those critical first 48 hours after a cyber attack, can be critical.
Do you worry your company won't know how to recover after a cyber attack? Has your business just been hit by ransomware and you're wondering what to do?
There's still hope.
Don't make the mistake of believing that your organisation will never be targeted. The right approach is to take proactive measures in advance - as it's not a case of whether your business will suffer the likes of a ransomware attack but when.
Make sure to read Exponential-e's step-by-step guide on ransomware remediation.
What's happened?
Recorded Future has reports that the British Government is proposing sweeping change in its approach to ransomware attacks.
Do you know Dmitry Yuryevich Khoroshev?
If you do, there's a chance that you might well on the way to receiving a reward of up to $10 million.
Law enforcement agencies across the US, UK, and Australia have named Dmitry Yuryevich Khoroshev as the mastermind behind the notorious LockBit ransomware group, estimated to have extorted $500 million from companies worldwide.
To Test or Not to Test? - When it comes to IT disaster recovery and remediation processes, regular testing is not a 'nice to have' - it's absolutely essential!
This isn't hyperbole on my part. You just have to look at the news on any given day. We've all heard the horror stories of organisations in both the public and private sectors experiencing prolonged downtime during disasters due to inadequate preparation, lack of testing, and the unsuitability of their legacy remediation processes and systems.
The international hotel chain Omni Hotels & Resorts has confirmed that a cyberattack last month saw it shut down its systems, with hackers stealing personal information about its customers.
In the aftermath of the attack, hotel guests reported that they had been forced to check in on paper, that room keys didn't work, and all phone systems and Wi-Fi were offline.
On the 18th March 2024, the Information Commissioner's Office issued its updated guidance around the issuing of fines when organisations have been found liable for the integrity of their customers' or end users' data being compromised. It is already well-established now that failure to ensure critical data remains secure will result in costly fines, as we have seen repeatedly in multiple high-profile cases over the years.
In October 2023, the British Library suffered "one of the worst cyber incidents in British history," as described by Ciaran Martin, ex-CEO of the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC).
The notorious Rhysida ransomware gang broke into one of the world's greatest research libraries, encrypting or destroying much of its data, and exfiltrating 600 GB of files, including personal information of British Library staff and users.
Any organisation that has tried to recover from a ransomware attack knows that it can be time-consuming and costly. Companies hit by an attack must choose between paying a ransom or recovering encrypted data from a backup.
Unfortunately, ransomware gangs are too aware that they can leverage significantly higher ransoms from their corporate victims if they have also compromise the company's backups. For this reason, we are seeing more and more cyber attacks targeting backups because they know that organisations desperately need them to recover if they want to avoid paying a ransom to cybercriminals.
Ransomware is malware that encrypts an individual's files so that they no longer have access to them, and subsequently demand payment for the files to be released. Usually the payment is asked to be made in an untraceable cryptocurrency form, such as Bitcoin. The most common way ransomware ends up on an individual's computers is through email spam, which individuals will click on and open.
Unfortunately, the files cannot be decrypted without a mathematical key which is only known by the cyber attacker, and the reason why many individuals tend to pay up. However, many find that despite paying the ransom, their files remain encrypted.
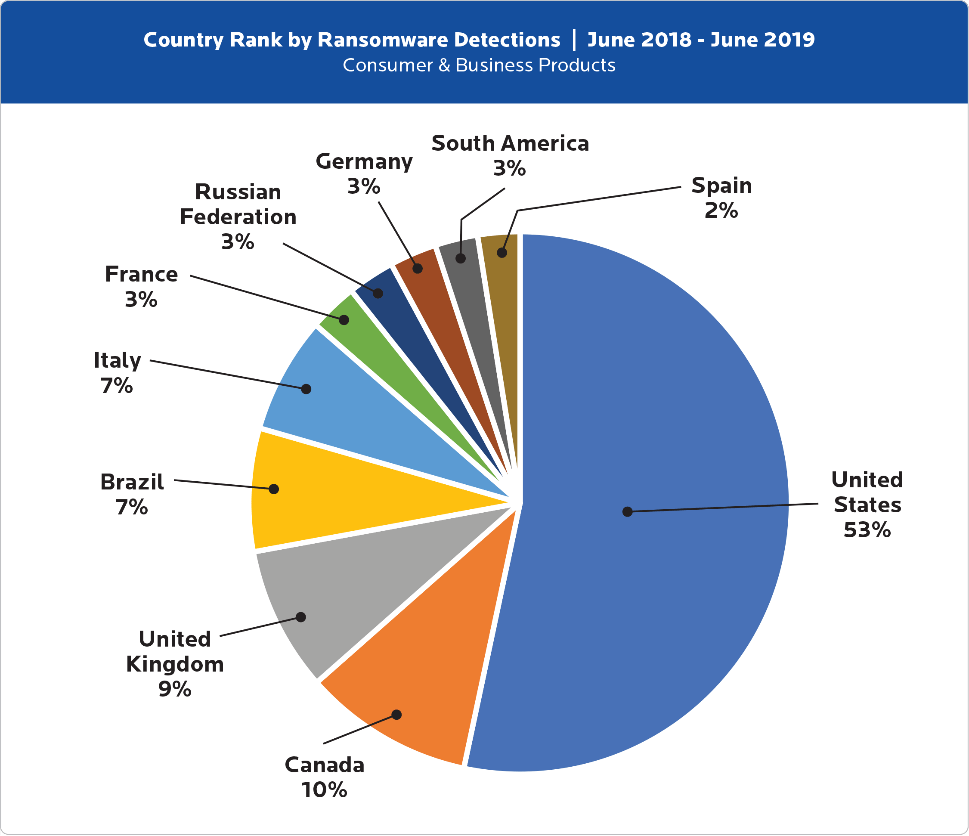
When looking at which countries were affected by ransomware attacks the most, the UK was found to have the highest percentage out of Europe:
Figure 1: Cybercrime Tactics and Techniques: Ransomware Retrospective Report, Malwarebytes
Despite the NHS facing one of the worst ransomware attacks in May 2017 - the WannaCry ransomware attack - which cost the NHS £92m and caused more than 19,000 appointments to be cancelled (The Department of Health), this chart clearly highlights how organisations in the UK still need to invest more into their Cyber Security solutions to stay protected from ransomware attacks.
At Exponential-e, we help organisations that have been affected by ransomware attacks. Our Head of Cyber Consultancy, Mark Belgrove, discusses a real-life cyber attack in the video below, and shares how Exponential-ehelped mediate the situation.
Passwords are often more associated with individual and consumer cyber security, but they are an essential part of an organisation's overall security posture. For example, you wouldn't leave the windows open overnight as this would allow easy access into the building for thieves. In the same way, a weak password offers cyber attackers easy access to your corporate infrastructure, after which they can use these credentials to escalate permissions until they granted themselves administration privileges, at which point the risk of financial and reputational damage becomes truly serious!
With the flexible office model slowly but surely supplanting the traditional working environments in favour of dynamic co-working spaces for a number of years now, we have seen many organisations reconsider the way they think about commercial real estate.
The past year has challenged the UK's education sector in ways that would previously have been inconceivable, with children learning from home the majority of the time since March.
In spite of the ongoing evolution of cyber security processes and technology, human error is still responsible for 95% of data breaches1. Phishing attacks alone represent a particularly insidious risk, with 91% of organisations experiencing a successful attack in 2021 alone2.
In light of recent geopolitical events, and the increased threat to corporate infrastructure, organisations across the UK must assume that they will be forced to contend with a cyber-attack in the near future and prepare accordingly. Indeed, the NCSC has already set out its own guidance to help organisations bolster their defences, which we strongly advise you to read and implement.